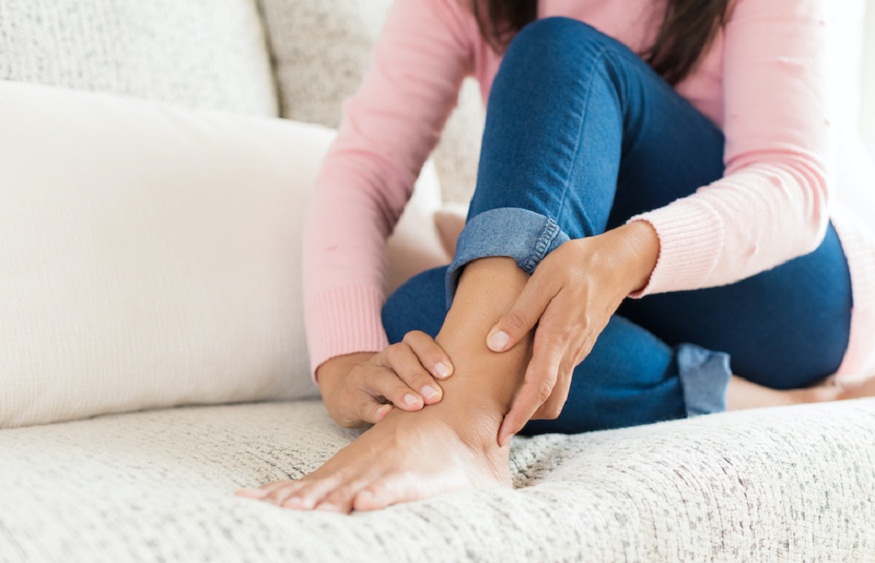

Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) affects blood flow to the limbs, often leading to discomfort and mobility issues. Podiatry plays a key role in managing PVD. It focuses on the health of feet and ankles, which are often the first areas impacted by poor circulation. By addressing symptoms early, podiatrists can help prevent complications and improve quality of life. Techniques such as Mission Viejo foot and ankle surgery may be part of the solution. Understanding the impact of podiatry in PVD management is crucial for effective treatment.
Understanding Peripheral Vascular Disease
PVD is a condition where blood vessels outside the heart and brain narrow, block, or spasm. This can affect the arteries, veins, or lymph vessels. Often, it arises due to a buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries, known as atherosclerosis. This buildup restricts blood flow, leading to pain and cramping, especially in the legs.
Symptoms of PVD include:
- Pain or cramping in the legs during physical activity
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Coldness in the lower leg or foot
- Sores or wounds on toes, feet, or legs that heal slowly
For further details, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute provides comprehensive information on the symptoms and causes of PVD.
The Role of Podiatry in PVD Management
Podiatrists are specialized in dealing with disorders affecting the foot, ankle, and lower extremities. Their expertise is vital in managing PVD because the feet are typically the first to show signs of poor circulation.
Key interventions by podiatrists include:
- Regular foot examinations to detect early signs of PVD
- Wound care to prevent infections from cuts or blisters
- Advice on proper footwear to improve comfort and function
These steps are essential in managing symptoms and preventing serious complications like ulcers or gangrene.
Benefits of Podiatry in PVD Treatment
By integrating podiatry into PVD treatment plans, patients often experience better outcomes. Here’s a comparison of outcomes with and without podiatric intervention:
| Outcome | With Podiatry | Without Podiatry |
| Pain Management | Improved | Limited |
| Wound Healing | Faster | Slower |
| Quality of Life | Higher | Lower |
The table shows that patients receiving podiatric care often report less pain and faster wound healing. This leads to an improved quality of life.
Integrating Surgical Solutions
Sometimes, conservative treatments are not enough. In such cases, surgical options become necessary. These procedures can restore blood flow and relieve symptoms significantly.
Surgical interventions might include:
- Angioplasty to widen narrowed blood vessels
- Bypass surgery to reroute blood flow around a blocked artery
- Endarterectomy to remove plaque buildup in the artery
Each procedure aims to improve circulation, thus alleviating symptoms and preventing severe complications.
Conclusion
Podiatry is an integral part of managing Peripheral Vascular Disease. By focusing on foot health, podiatrists can prevent and manage symptoms effectively. Early intervention and regular care can make a significant difference in outcomes. For those needing more advanced care, surgical options offer relief and improved quality of life. Understanding and utilizing podiatric care in PVD treatment ensures comprehensive management of this chronic condition.
 Tennessee Men’s Clinic Discusses the Correlation of Healthy Relationships to Men’s Health
Tennessee Men’s Clinic Discusses the Correlation of Healthy Relationships to Men’s Health  Frequently Asked Questions About Speech Therapy Answered
Frequently Asked Questions About Speech Therapy Answered  The importance of choosing a good gynaecologist doctor for your health
The importance of choosing a good gynaecologist doctor for your health  Ophthalmologists’ Strategies For Managing Chronic Eye Diseases
Ophthalmologists’ Strategies For Managing Chronic Eye Diseases  The Role Of Cardiologists In Managing Chronic Heart Failure
The Role Of Cardiologists In Managing Chronic Heart Failure  Breaking Down Barriers: An Infertility Specialist’s Approach To Inclusive Treatment
Breaking Down Barriers: An Infertility Specialist’s Approach To Inclusive Treatment  Complete Trekking Guide to Langtang and Annapurna
Complete Trekking Guide to Langtang and Annapurna  Trek Nepal’s Four Great Regions: Annapurna, Langtang, Manaslu, and Nar Phu:
Trek Nepal’s Four Great Regions: Annapurna, Langtang, Manaslu, and Nar Phu:  The Ecosystem of Ease: How Bill Payments Evolved into a Digital Habit
The Ecosystem of Ease: How Bill Payments Evolved into a Digital Habit  How Insurance Apps Are Embedding Themselves Into India’s Daily Payment Flows
How Insurance Apps Are Embedding Themselves Into India’s Daily Payment Flows